| erf(0)=0 erf(0.025)=0.028204 erf(0.05)=0.056372 erf(0.075)=0.08447 erf(0.1)=0.11246 erf(0.125)=0.14032 erf(0.15)=0.168 erf(0.175)=0.019547 erf(0.2)=0.227 erf(0.225)=0.24967 erf(0.25)=0.27633 erf(0.275)=0.30266 erf(0.3)=0.32863 erf(0.325)=0.35421 erf(0.35)=0.37938 erf(0.375)=0.40412 erf(0.4)=0.42839 erf(0.425)=0.45219 erf(0.45)=0.47548 erf(0.475)=0.49826 erf(0.5)=0.5205 erf(0.525)=0.54219 erf(0.55)=0.56332 erf(0.575)=0.58388 erf(0.60)=0.60386 erf(0.625)=0.62324 erf(0.65)=0.64203 erf(0.675)=0.66022 erf(0.70)=0.6778 erf(0.725)=0.69478 erf(0.75)=0.71116 |
erf(0.775)=0.72693 erf(0.8)=0.7421 erf(0.825)=0.75668 erf(0.85)=0.77067 erf(0.875)=0.78407 erf(0.9)=0.79691 erf(0.925)=0.80918 erf(0.95)=0.82089 erf(0.975)=0.83206 erf(1.0)=0.8427 erf(1.05)=0.86244 erf(1.10)=0.8802 erf(1.15)=0.89612 erf(1.20)=0.91031 erf(1.25)=0.9229 erf(1.30)=0.93401 erf(1.35)=0.94376 erf(1.40)=0.95229 erf(1.45)=0.9597 erf(1.50)=0.96611 erf(1.55)=0.97162 erf(1.60)=0.97635 erf(1.65)=0.98038 erf(1.70)=0.98379 erf(1.75)=0.98667 erf(1.80)=0.98909 erf(1.85)=0.99111 erf(1.90)=0.99279 erf(1.95)=0.99418 erf(2.0)=0.99432 |
||||||||||||
| Cooling of a dike: Analytical vs Numerical solutions... | |||||||||||||
| Exercise 5: The analytical solution that describes the heat transfer through time across of a dike 2w meters wide is: | |||||||||||||
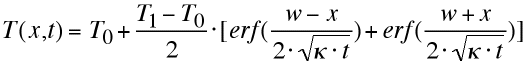 |
|||||||||||||
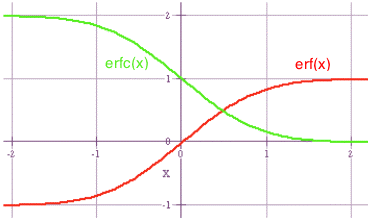
| erf(x) is the error function. It was first tabulated in the mid-1800's during the development of probability theory. Its properties are: erf(0)=0 erf(∞)=1 erf(-x)=-erf(x) The complementary error function erfc(x) is defined as: erfc(x)=1-erf(x) |
 |
||||||||||||
| An approximation of the error function is: 0≤x<0.6: erf(x)=x 0.6<x≤1.2: erf(x)=0.84+log(x) 1.2<x≤2: erf(x)=0.9+0.35.log(x) x>2: erf(x)=1 with erf(-x)=-erf(x) |
|||||||||||||
| • At the time of emplacement the material inside a 20 meter wide dike was at T1=900ºC whereas the surrounding host rock was T0=300ºC. Using the analytical solution above, calculate the temperature profile across the dike at a time t=1month, 1 year, 10 years after emplacement. (Diffusivity: 10-6 m2.s-1) | |||||||||||||
| • Build an Ellipsis model using a 1x6 box, level:4, temperature-independent viscosity (η 0=2500). The dike, 0.2 thick, is centered at x=3. Background temperature: 300ºC, temperature in the dike: 900ºC. Since lengths are divided by 100 the diffusivity must be scaled to maintain the representativity of the model. This scaling can be done by noting that the dimension of diffusivity is m2.s-1. Since the scaling factor for length (m) is 10-2 that of surface (m2) is (10-2)2. The analytical solution tells us that T(x, t) is depends on x/(2.√ (λ .t)). The temperature is not affected by reducing the numerator as long and the denominator is reduced by the same proportion. Compare the analytical and numerical solutions. | |||||||||||||