|
|
|
The elastic-plastic-viscous lithosphere |
|
|
The application of the elastic beam theory is limited to ponctual to linear load problems including foreland basins in continental crust. Only for these problems the lithosphere can be approximated by an elastic plate. In reality the mechanical behavior of the Earth's lithosphere is considerably more complex than that a simple elastic body and involves brittle as well as as ductile flow depending on parameters including pressure, temperature, and strain rate.
|
|
|
| Brittle failure- • Joints, extensional fractures (A), veins, and dikes (B) are an expression of brittle failure at low differential stress (σ d). At low differential stress fratures develop perpendicular to the minimum stress axis σ 3. At high differential stress shear fractures, faults (normal, reverse, strike-slip), are the manifestation of brittle failure. Shear fractures contain the intermediate stress axis σ 2 hence, σ 1 and σ 3 are in the plane normal to σ 2 perpendicular to the fault plane. |
|
|
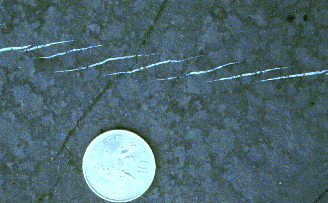
| A/ Extensional fractures in a limestone. The fractures are filled with fibrous calcite oriented perpendicular to the veins therefore parallel to σ 3. |
|
 |
C/ Shear fractures in a Zebra rock (shale) from the Kimberleys (WA). The upper part of the sample shows reverse shear fractures whereas the lower section displays normal shear fractures. Clearly this set argues for a switch in the tectonic regime. The sample is 8 cm wide. |
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
|
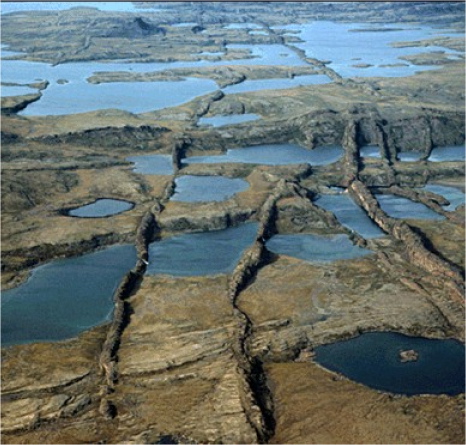
D/ Brand new high angle normal fault (southwest USA)... |
|
 |
|
|
|
B/ Intrusion of dykes into marine sandstones. The dykes are about 30 cm wide. Dykes involves surface extension in a direction perpendicular to the dykes. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



