| CONTINENTAL BREAKUP | 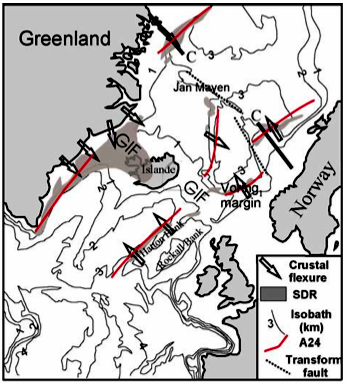 |
|||||||
| Geometric aspects of continental breakup: How do continents break ? | ||||||||
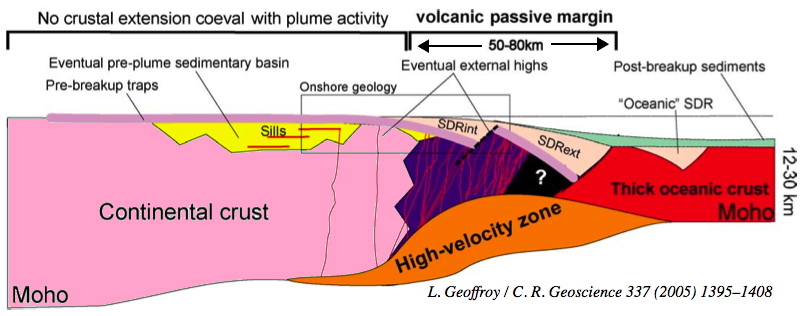
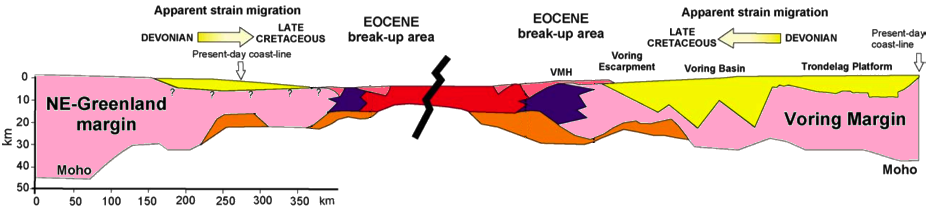
| Example of volcanic margin: Following continental break-up, enhanced mantle melting lead to thicker than normal oceanic crust. The thickness of the oceanic crust along the Greensland-Iceland-Faereo ridge reaches 40 km. Seaward dipping seismic reflectors (SDR in the X-section below) are syn-magmatic roll-over above continentward dipping normal faults. The crust beneath SDR is heavely intruded by dikes and underplated by mafic rock (high-velocity zone). Sketches from L. Geoffroy, 2005, C.R. Geoscience, 337. |
||||||||
 |
||||||||
 |
||||||||